Road Saw Guide: What It Is & How Deep It Can Cut
Construction projects often need precise cutting. A road saw makes this possible. It is a serious and powerful equipment. It efficiently sliced through concrete and asphalt. Saws on the road are popular with highway repairs, bridge work and city street work.
They provide workers with clean lines, neat trenches and precise openings. Depth is one of the most things you need to look for when you are picking out a saw. If the saw will not reach the needed depth, the job will not be completed.
This can lead to delays, squander money and destroys equipment. If you are working to cut asphalt for maintenance. It also cut concrete for road enhancements; depth makes the difference.
If you are cutting asphalt for utilities or cutting concrete for roadwork, being aware of the limits of a road saw results in efficiency, safety generic medication and cost control is important. This article will help yourself in familiarizing with the capabilities of a road saw.
Contents
What Is a Road Saw
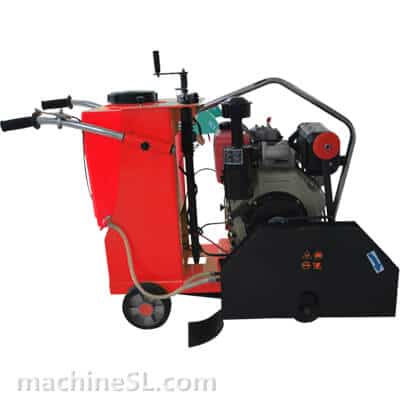
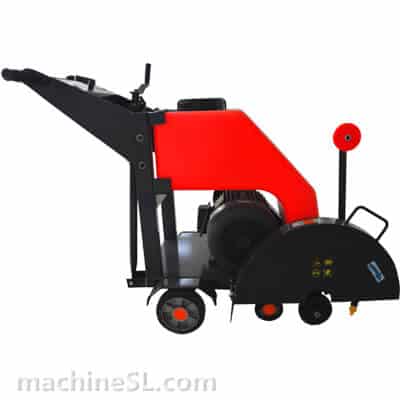
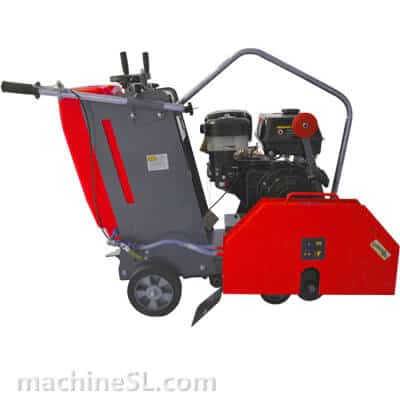
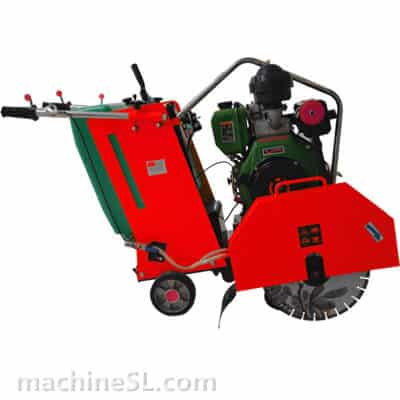
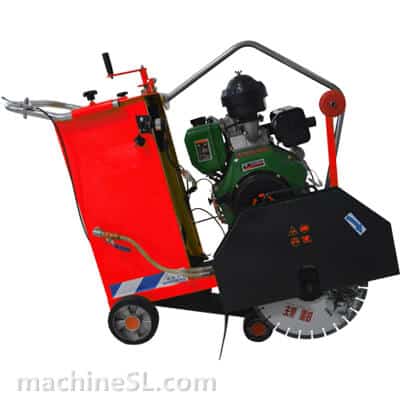
A road saw is also known as a floor saw, slab saw or concrete/asphalt saw. It is a rugged machine for even, flat surfaces. It is a lot more powerful than manual tools such as hand-held grinders or hand saws.
Common Uses
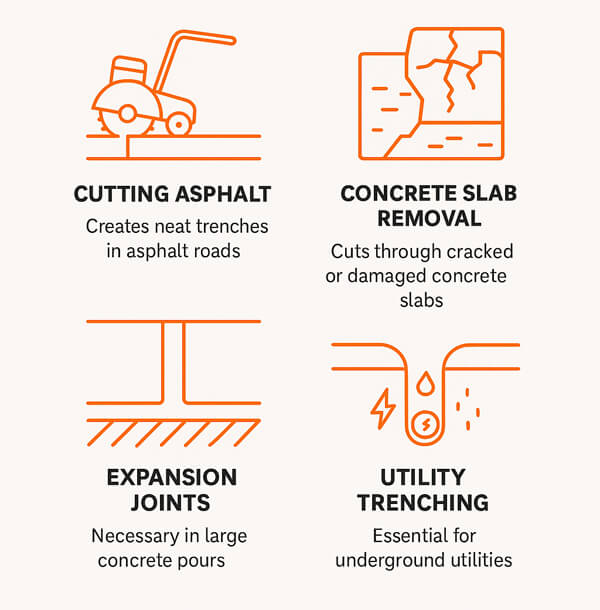
By name, it is clear that the road saw is used for cutting road. But here are some common use are as below:
- Cutting asphalt: Workers cut neat trenches for drainage or pipe installation.
- Concrete slab removal: Cracked or aged concrete is broken out so that a replacement can occur.
- Expansion joints: Enormous concrete pours require joints so as to minimalize cracking.
- Utility trenching: Most water pipes, gas lines and cables lines can be found under roads.
Types of Road Saws
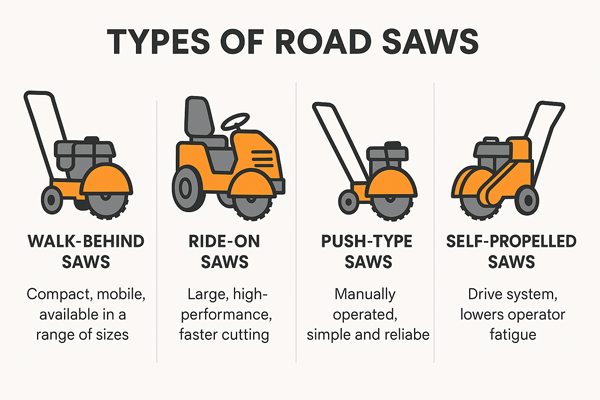
There are following three types of road saw as below:
- Walk-behind saws: The most common type. Compact, mobile, and available in many sizes.
- Ride-on saws: Bigger and faster. Best for airports, highways, and large projects.
- Push type: Operator pushes the machine forward manually.
- Self-propelled: The unit moves itself, lowering operator fatigue.
Key Components
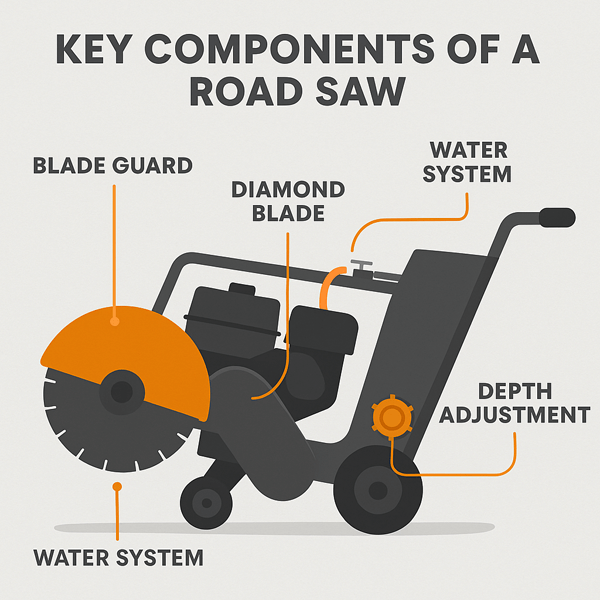
A road saw is comprised of the following components:
- Blade guard: It is a shield to guard against thrown material.
- Diamond blade: The main cutting part. Segments are made for concrete or asphalt.
- Water system: Pumps water to the blade, cooling it and reducing dust.
- Depth: Allows the operator to insert pointed blade at correct depth.
Road saws are available in a variety of sizes. They have only one thing in common. They all chop tough materials in a safe, efficient manner.
How a Road Saw Works
The saw uses an engine or motor to spin the diamond blade. The spinning blade slowly lowers into the material and cuts as the machine moves forward. For different type of cutting, it works differently.
Wet vs Dry Cutting

As we have two types of cuttings, here are the methods to use a road saw for both.
- Wet cutting: Keeps the blade cool. Controls dust. Makes the cut smoother. Recommended for most jobs.
- Dry cutting: Used when water is not allowed. Works for short, shallow cuts. Creates more dust and heat.
Blade Selection Factors
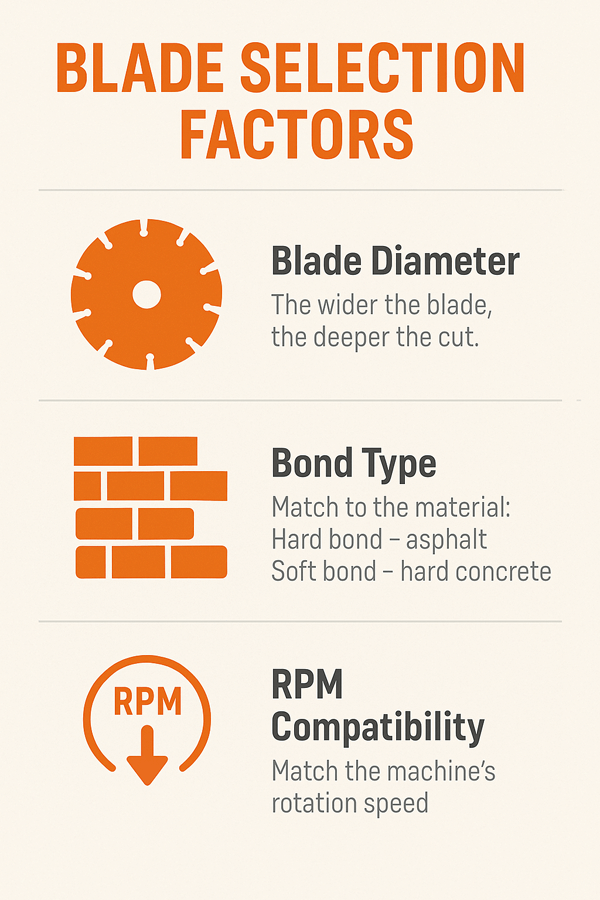
When all the factors are balanced the saw moves in a smooth way. The operator escorts the machine but the blade is the hard-working element. While selecting a blade for road saw, keep the below points in mind.
- Blade diameter: The wider the blade, the deeper will be cut. Shallow cuts take small blades.
- Bond type: Blade bonds must match the material. A hard bond is for asphalt. A soft bond is for hard concrete.
- RPM compatibility: A blade must match the machine’s rotation speed. Mismatch causes poor cutting and danger.
How Deep Can a Road Saw Cut
Depth of a cut while using a road differs according to the purpose and type of road saw. Generally, we have a range of cutting depth as below:
General Cutting Depth Ranges
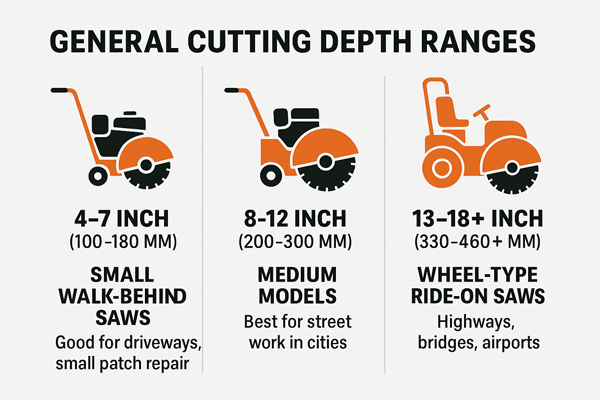
- Small walk-behind saws: This type of road saw can cut 4‐7 inch (100‐180 mm) deep. It is good for driveway and small patch up.
- Medium models: Medium Road saws are capable of cutting 8—12 in (200—300 mm) deep. Street work in the city is the best application.
- Wheel type ride-on road saw: A ride on road saw can cut up to 13–18+ inch (330–460+ mm). It can be applied for highways, bridges and airport.
Factors that Impact Cutting Depth Blade
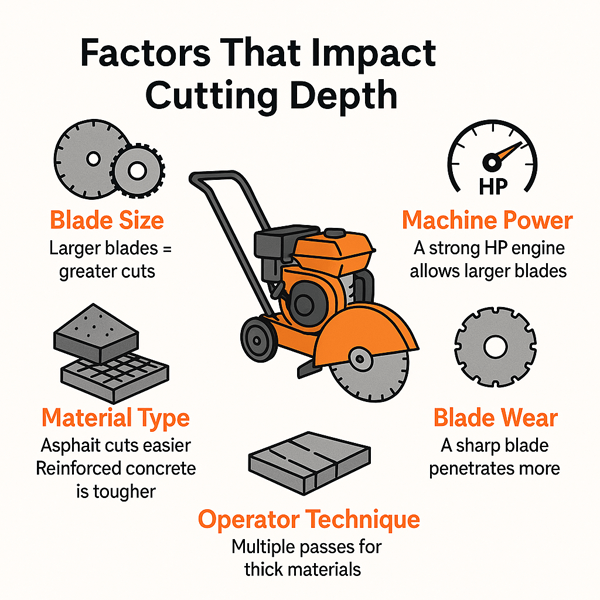
A cut can depend upon various factors for its depth. It can be machine type, material type and others. Some of the factors that impact the cut depth are:
- Blade size: Larger blades = greater cuts.
- Material type: Asphalt cuts easier. Reinforced concrete is stronger and tougher.
- Machine power: A strong horse power engine also manage large blade.
- Blade wear: A sharp blade penetrates more. An old blade decelerates and is less effective when cutting.
- Operator technique: Thick materials often need multiple passes instead of one deep cut.
Formula Reference
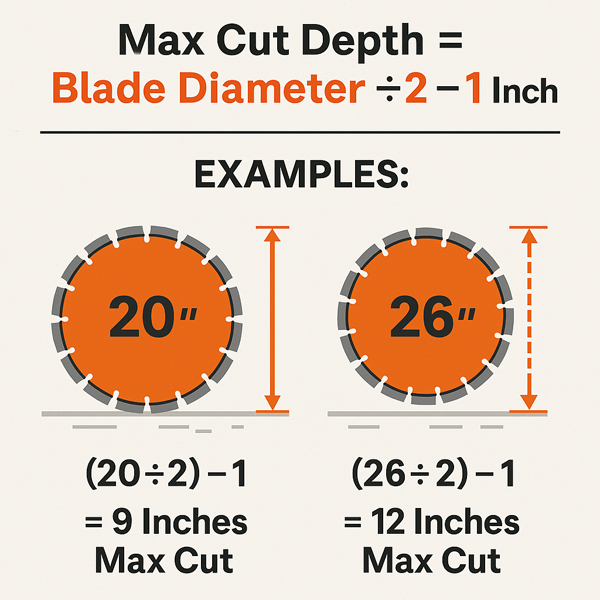
A simple rule: Max cut depth ≈ Blade diameter ÷ 2 – 1 inch. The “–1 inch” accounts for the blade guard and arbor hole.
Example: A 20 in blade will cut down about 9 inch deep. A 26-inch knife blade will cut about 12 inches.
Choosing the Right Road Saw for Your Cutting Depth
Choosing the correct saw prevents failure and saves money.
- Road repair: A medium saw with 8–12-inch depth works best.
- Utility trenching: Go for 12–16 inches. Trenching often needs deeper cuts.
- Deep slab removal: Only large ride-on saws with 16+ inches will do.
Mobility and Site Constraints
- Small walk-behind saws fit in narrow streets or tight work zones.
- Ride-on saws are ideal for wide, open areas.
Power Source Selection
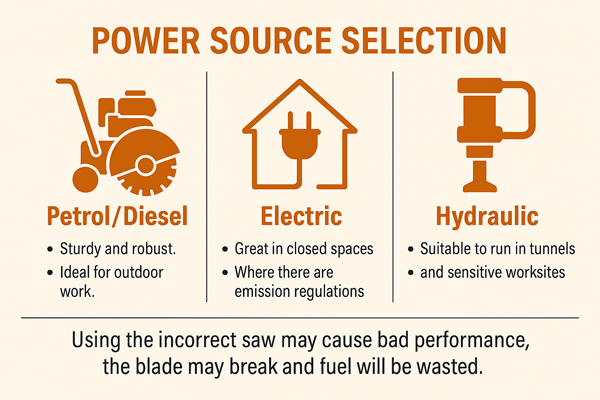
- Petrol/Diesel: Sturdy and robust. Ideal out-of-doors work.
- Electric: Great in closed houses or where there are emission regulations.
- Hydraulic: Suitable to run in tunnels and sensitive worksites.
- Using the incorrect saw may cause bad performance, the blade may break and fuel will be wasted.
Tips for Achieving Maximum Cutting Depth Safely

A good skill and care is necessary to get the deepest cut. Select an appropriate blade to the material. Trained operators will never fail to listen to the blade sound. Changes in sound warn of overheating or binding.
- Every time, choose a blade that is suited to the material. Asphalt blades are different to concrete blades. Asphalt and concrete are different in the type of bonds required.
- Trained operators can never ignore blade sound. Cutting is normal when there is a smooth sound. An acute or shrill sound indicates that it is overheating.
- Diamond blades do not take a lot of heat. Water blades to moisten constantly. Water diminishes dust, enhances vision and safeguards employees. Avoid long cut of dry.
- Begin with small incisions and use those to direct more profound incisions. This eliminates the tendency of the blade to go off line.
- Do not force the saw too much. Let the knife do. Making the machine bite the blade warps it and decelerates cutting.
- Before all uses, examine blades. Search the loss of segmentation, presence of cracks and uneven wear. Make sure that the arbor hole is snug.
- The saw is straight when the saw is guided with a steady hand. The uneven cuts are produced by jerky movement. Beware of shaking and jerking. Where the saw sticks, at a cut, check and restart.
- To cool blades, do this when the projects are long. Have short rest after deep passes. Wear can be saved by the use of multiple blades which operate by rotation.
Safety Precautions When Using a Road Saw
It is critical to be safe. Road saws are noisy, bulky and rapid. Following are some safety rules that can make the operation risk-free.
Safety Rules

- PPE: Wear helmet, glasses, ear protection, dust mask, gloves.
- Before starting place the blade guard on.
- Seal off the area of work. Have cars and pedestrians clear.
- Maintain the maximum depth of manufacturers.
- Stay alert to kickbacks, vibration, or sudden stops.
Even trained operators must follow rules. Road saw accidents can be serious.
FAQs
Can I increase depth by changing the blade?
Yes. But only if the saw supports a larger blade. Machine power and design limit blade size.
What’s the deepest a road saw can cut in one pass?
Around 18 inches for the largest ride-on models. Beyond that, operators must cut in stages.
Do I need multiple passes for reinforced concrete?
Yes. Reinforcement bars slow progress and wear blades. Multiple shallow passes are safer.
How does asphalt vs concrete depth differ?
Asphalt is softer. Saw cuts are quicker and deeper. Concrete, especially reinforced, takes longer.
What’s the difference between a road saw and a wall saw?
Road saws cut flat surfaces like roads. Wall saws cut vertical surfaces like walls or panels.
Conclusion
Road and construction work cannot be done without road saws. They precision-cut asphalt and concrete fast. The depth of cutting will vary with size, power, and the hardness of material using the blade. The operator’s skill also matters.
For small repairs, a walk-behind saw works well. Ride-on saws are required in the case of deeper trenching or removal of large slab formation. Always equip the machine and blade to the task. This avoids accidents, times and blades long life. Depth is as necessary as safety.
Wear protection equipment, obey the regulations and do not overload the machine. In deep and complicated projects safest is the use of professional operators. They come with experience and expertise and the appropriate gear.


















Leave A Comment