Why Roads Are Cut with Lines and Grooves
Roads are not just flat black surfaces. They are engineered systems built to handle stress, weather, and traffic. One hidden design feature is road cutting and grooving.
Drivers see these cuts on highways, city roads, intersections, and bridges. They appear as thin lines, shallow grooves, or wide slots. To many people, they look like random scratches.
But these cuts are far from random. They are carefully planned by road engineers. Each line plays a role in safety, drainage, or road life.
They make roads stronger. They prevent accidents. They help manage modern traffic. Without them, roads would fail much faster. And driving would be far more dangerous.
In this article we will explore road grooving and cutting. It will cover all the aspects such as: types, purpose, methods, and benefits etc.
Contents
Understanding Road Grooving and Cutting
Road grooving is the process of cutting small channels into pavement. Road cutting refers to deeper, structural cuts made during construction. Both are crucial for road design.
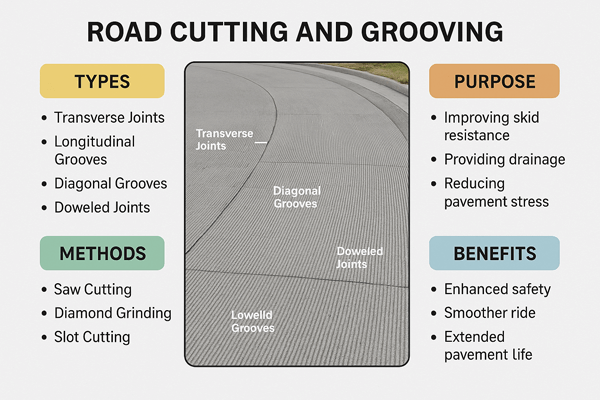
There are several main types of road cutting. For example:
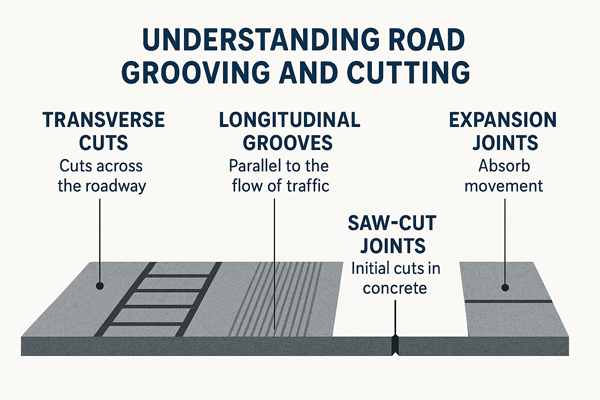
- Transverse cuts: These cuts across the roadway to regulate cracking. dispersion of heavy loads. They channel the stress into secure courses. These cuts avoid some unguided demolition on roads and bridges.
- Longitudinal grooves: These are parallel to the flow of traffic. They enhance traction. Longitudinal grooves remove water out of tires, decrease hydroplaning. These grooves also ensure high-speed roads are safe.
- Expansion joints: These are cracks on bridges and slabs which absorb movement. They stop buckling during hot weather and cracking during cold weather.
- Saw-cut joints: The joints that are the initial cuts on a new concrete . They direct shrinkage cracks. They maintain pavements smooth, robust and devoid of untidy random fractures.
Each type solves a different engineering challenge. Together, they protect the road from heavy loads, water, and heat.
Grooves may be invisible to most drivers. But they are always working silently under the tires.
The Main Reasons for Cutting Lines in the Road
For roads, there may be many different reasons to cut lines. It can be structural, safety, design or any other. Some of the common reasons have been discussed as:
Safety Enhancements
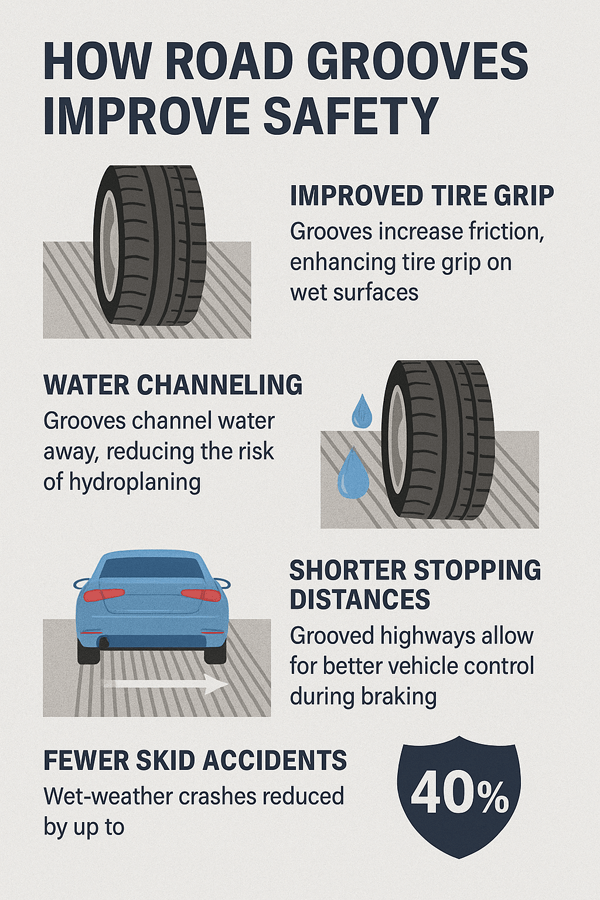
Safety is the top reason. Grooves improve tire grip. They channel water away from the surface. This reduces hydroplaning at high speeds.
On highways, grooves shorten stopping distances. They give drivers more control in emergencies. Skid accidents are greatly reduced.
In fact, research shows that grooved highways cut wet-weather crashes by up to 40%. This proves their value as a life-saving feature.
Drainage and Water Management
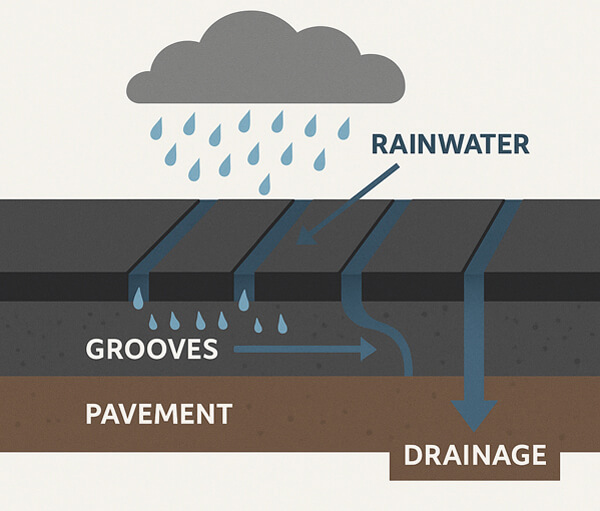
Water destroys roads quickly. It seeps into cracks and weakens the base. It creates potholes and surface failures.
Grooves act like tiny drainage canals. They move rainwater off the surface. This keeps pavement drier and stronger.
Drainage is especially vital on bridges. Without grooves, water would pool and cause structural damage.
Crack Control and Pavement Longevity
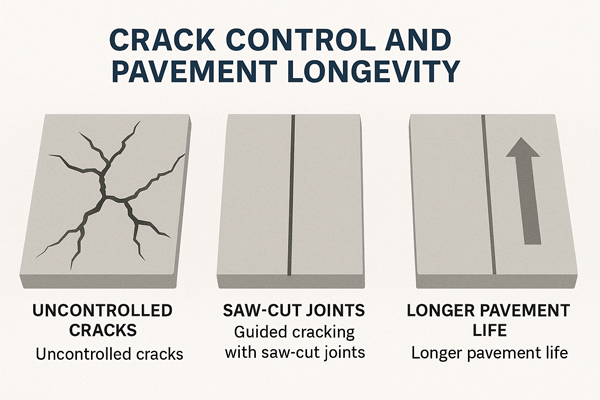
Concrete always cracks. But uncontrolled cracks are unpredictable. They weaken roads and cause dangerous bumps.
Saw-cut joints guide cracks into neat lines. This keeps them harmless and controlled. It also improves the appearance of the road.
Planned joints extend pavement life by decades. They reduce costly repairs and road closures.
Bridge and Pavement Expansion
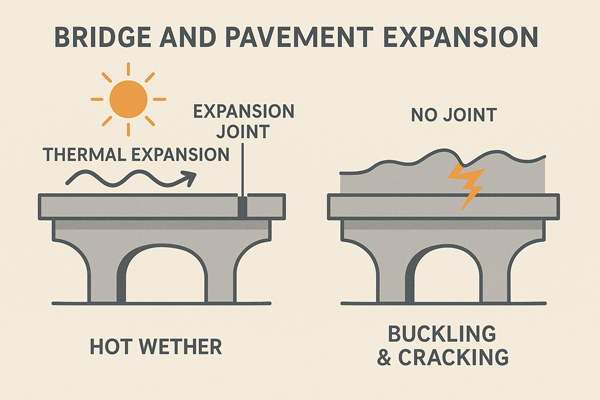
Concrete and steel expand in heat. They shrink in cold. This constant movement can warp surfaces.
Expansion joints absorb that movement. They prevent buckling during heat waves. They also protect bridges from stress.
Without expansion cuts, bridges would crack and fail. This shows how small grooves protect huge structures.
Surface Noise and Vibration
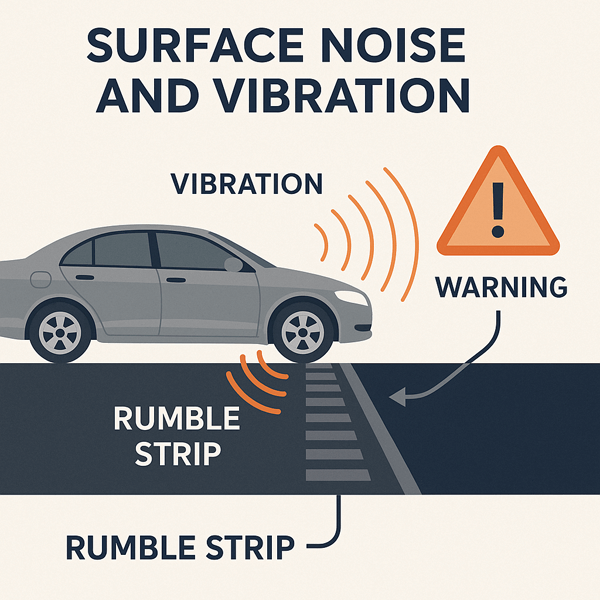
Some cuts are designed to make noise. These are called rumble strips. They vibrate tires and create sound.
Rumble strips wake sleepy drivers. They warn about curves and toll areas. They also reduce accidents on rural highways.
Sensor Installation
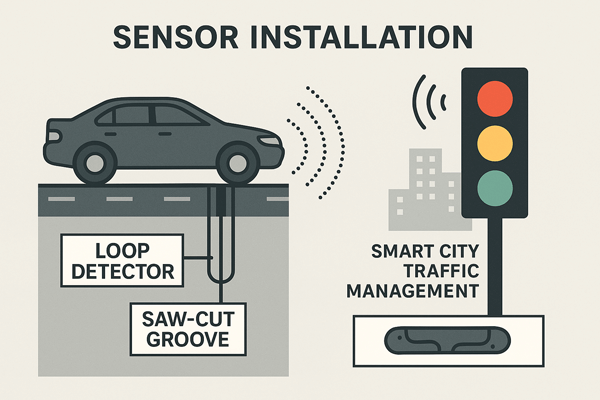
Grooves also hide technology. Cities place loop detectors inside saw cuts. These sensors count vehicles and track flow.
They send data to traffic lights. Signals then adjust automatically. This reduces congestion and saves fuel.
Smart cities depend on these hidden cuts. They turn old roads into intelligent transport systems.
Preventing Ice Formation
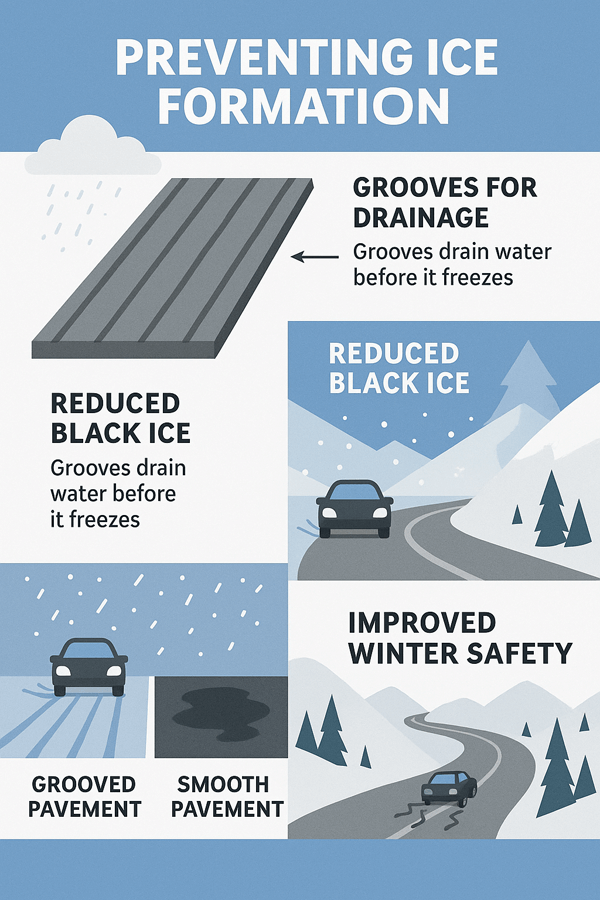
Ice makes roads deadly in winter. Grooves drain water before it freezes. This reduces black ice on the surface.
On mountain highways, grooved pavement is critical. It prevents vehicles from sliding out of control. It saves lives in cold weather conditions.
How Road Grooving and Cutting Is Done

Road cutting is not random. It is a careful process with advanced tools. The proper process and tools should be adopted to execute operation safely.
Workers use diamond blade saws for precision. Diamond is strong enough to cut through asphalt and concrete. Other machines include walk-behind cutters and milling machines.
The process includes:
- Mark cut lines with chalk or laser guides. Accurate marking ensures the cut follows the planned alignment without deviation. Laser guides give higher precision, especially for long or straight cuts. Clear marking also reduces rework and improves efficiency.
- Adjust depth for exact specifications. Depth control is critical to match the required thickness of concrete or asphalt removal. Setting the blade at the right depth prevents structural damage to the base layers. It also ensures compliance with engineering design standards.
- Water controls detrimental dust affecting the on-site health and visibility of workers. It also cools the blade and decreases the wearing and prolongs the life blade. This is done so that the cutting process is smoother and safer.
- Cleaning the road by vacuuming wastes. Remove debris in real time and stave off worker safety and adjacent traffic. It is also used as surface exposure to further stages of building as resurfacing and sealing.
- Safe working environment enhances the quality of the projects and also improves safety. It is the key to all. Employees have helmets, gloves and Goggles. Traffic is often redirected for protection. Every cut is measured, clean, and precise. This ensures the road performs as designed.
Different Types of Road Grooving Techniques
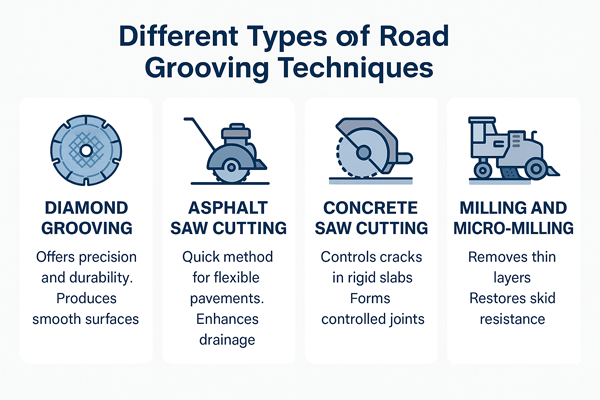
There are multiple cutting methods. Each method is specifically used for the concerned purpose. It carries unique characteristics, and purposes. Following are the grooving methods in roads.
- Diamond Grooving: The diamond grooving offers a precision. It is durable in a specialized manner in producing smooth surfaces. It has been used country wide especially in busy roads.
- Asphalt Saw Cutting: This is an efficient method. It is reckoned with in terms of its speed especially when utilized on flexible pavements. It assists in rapid forming of clean grooves thus asphalt saw crews are in service where the draining of water can be performed better. There are lesser chances of hydroplaning.
- Concrete Saw Cutting: Concrete Saw cutting is specifically applied to the control of cracks in stiff concrete slabs. Formation of controlled joints can aid in prevention of undesirable crack making. The road to have good structures which can hold up under changing environments.
- Milling and Micro-Milling: This is done to eliminate thin layers of the pavement. They have been in use to restore skid resistance in the pavement and road safety. Micro-milling is a more refined process. It is ideal to restore smoother surfaces and/or increase grip.
Each technique has advantages. Diamond grooving creates the smoothest finish. Milling is faster and cheaper for large areas. Engineers choose based on cost, road type, and climate.
Where and When Road Cuts Are Most Common

Cuts appear at many stages of road work. Such as:
- During new construction: Cuts are strategically designed from the beginning. It ensure optimal performance and longevity of the pavement.
- In rehabilitation projects: Grooves are applied to restore the necessary grip on worn-out surfaces.
- Before resurfacing: Cuts are made to improve the bond between the existing surface and new layers.
- On bridges: Grooves are incorporated into the bridge deck to prevent water buildup.
- At intersections: Saw cuts are used to hold traffic sensors in place.
They are also common on mountain roads. Here, drainage grooves stop water and snow damage. Every location has its own engineering reasons.
Benefits of Cutting Lines in the Road
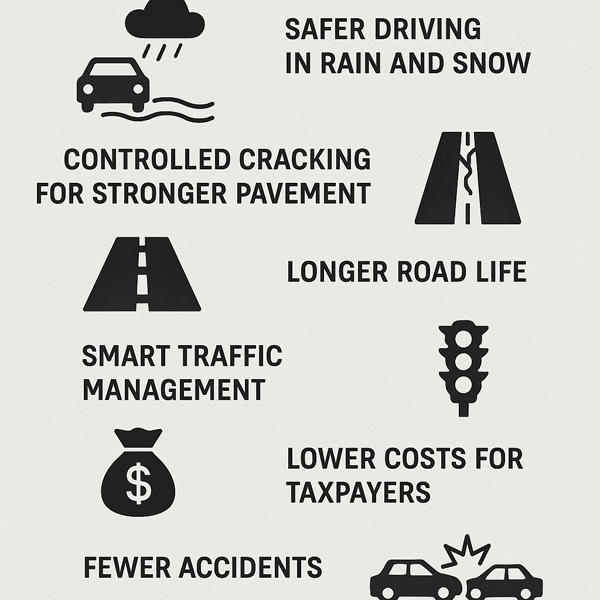
The benefits of cutting the lines on road are broad and long-lasting. It provides:
- Safer driving in rain and snow.
- Controlled cracking for stronger pavement.
- Longer road life with fewer repairs.
- Smart traffic management through sensors.
- Lower costs for taxpayers.
- Fewer accidents from skidding or drifting.
Cuts are small features with massive impact. They save money. They save lives.
Common Misconceptions About Road Cuts

Many people misunderstand grooves. Here are the facts:
- Myth: “They are random cracks.” Fact: They are planned and engineered.
- Myth: “They damage tires.” Fact: They protect tires by giving grip.
- Myth: “They are only decoration.” Fact: They serve critical safety purposes.
Grooves are not cosmetic. They are invisible guardians of road safety.
Environmental and Cost Considerations
Road cutting also respects the environment. Water-based cutting controls dust pollution. This protects nearby homes and workers.
Waste materials are not thrown away. Asphalt and concrete are recycled into new roads. This saves natural resources.
Grooving is also cost-effective. Preventive cutting is cheaper than repairing damaged roads. Every dollar spent saves many dollars in future repairs.
Cities worldwide invest in grooves to save money. They get stronger roads at lower long-term costs.
Conclusion
Road cuts may look small, but they are powerful. They prevent cracks, drain water, and manage traffic. They reduce accidents and extend road life.
They also protect bridges from buckling. They warn drivers with rumble strips. They even reduce black ice in winter.
Next time you drive, look at those lines. They are not random scratches. They are carefully designed engineering features.
They keep roads strong, safe, and smart. They save lives quietly, every single day.
Road grooves are the hidden protectors of modern transport.


















Leave A Comment