Road Roller Types, Components, Principles and Operation
Compaction is a critical activity the construction process. Whether in structural construction or in road construction, compaction plays an important role in durability and safety. To improve quality and minimize construction costs, the use of compaction equipment is encouraged. Road rollers are some of the common and most used equipment in construction today.
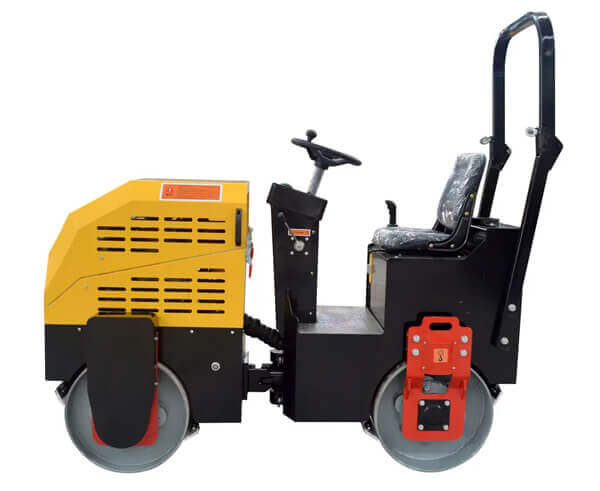
Road rollers are equipment, either handheld or driven that have a weighted drum at the front or back. The drum is rolled over construction material to compact it to desired densities. In road construction, road rollers are used to compact material for strong and durable bases and subbases. They are also used in smoothing surfaces in asphalt paving.
Compaction in structures provides firm and stable grounds for foundation construction. Road rollers are used to compact different materials used in foundation construction.
Contents
Types of Road Rollers
Compaction applications are varied; while some structures require high degrees of compaction, others require minimum compaction force for structural soundness. The material considered and degree of compaction needed determine the choice of road rollers to be used.
Based on their operation mechanisms, road rollers are classified into two main types; these are static road rollers and vibratory road rollers.
Static road rollers
This type of road rollers relies solely on the weight of the drum to compact material. The absence of vibration mechanisms makes static road rollers easy to operate and maintain. Static rollers are suitable for most material apart from cohesive soils. The need for several passes to attain the required degree of compaction makes using static rollers expensive and time consuming.
Vibratory road rollers
Vibratory road rollers are most ideal for compacting granular materials. The drum on these rollers are fitted with eccentric weights that are triggered electronically to generate vibrations. The vibrations, coupled with the weight of the drum effects compaction to the required degree. Vibratory road rollers require less passes to attain required compaction. While passing over the material, the vibrations eliminate more air from the particles resulting in a denser material.
Despite the suitability and benefits, overusing vibratory road rollers could damage the material under compaction. Additionally, the vibrations generated by the roller could be destructive to the surrounding structures on site. The cost of maintaining vibratory rollers is higher since the eccentric weights and vibration mechanism need regular checking.
An expert is needed to ensure the roller doesn’t damage the material under compaction or the surrounding structures; this raises the cost of operation.
Components of a Road Roller
The working of a road roller is facilitated by several components, each playing a vital role in its operation. Below, we will discuss the essential parts and features of road rollers.
- Drum
The drum serves as the compaction interface between the roller and the material being compacted. It is a cylindrical structure made of heavy metal, enabling effective compaction. The weight of the drum forces the material particles close together, eliminating air voids. In vibratory rollers, the drum contains eccentric weights that generate vibrations. There are different types of drums available:
- Smooth drum: These drums have a smooth surface and are ideal for compacting granular soils. They exert uniform pressure, making them suitable for cohesive materials as well.
- Padfoot drums: These drums have cylindrical or rectangular shapes with protruding pad or feet-like structures. The pads create concentrated pressure points on the surface, making padfoot drums effective for compacting cohesive soils, clay, or other cohesive materials.
- Pneumatic drums: Pneumatic drums are hollow and made of rubber. They are filled with air or water. They are used for compacting asphalt and provide a smooth and uniform surface finish. The rubber material prevents surface damage and offers better traction.
- Engine and power train
The engine and powertrain are vital components of a road roller. The engine serves as the power source, commonly powered by diesel, gasoline, or electric motors. The transmission system transfers power from the engine to the wheels, enabling movement and control. Hydraulic controls play a crucial role in operating various functions, such as steering, braking, and vibrating mechanisms.
Together, these components ensure the efficient operation and maneuverability of the road roller on construction sites.
- Frame and axles
The frame and axles are crucial parts of a road roller, providing structural integrity, stability, and maneuverability. The frame serves as the backbone, supporting the weight of the roller and its components. Axles are responsible for transmitting power to the wheels and ensuring even weight distribution. Axle systems, such as tandem or articulated designs, allow for smooth movement and adaptability on uneven surfaces.
Suspension systems play a vital role in absorbing shocks and vibrations, enhancing stability, and ensuring consistent compaction performance.
Working Principles
Static road rollers
The working principle of a static road roller involves applying static weight to compact the surface. The roller’s heavy drum exerts pressure on the material beneath, compressing it and eliminating air voids. As the roller moves forward, the drum’s weight creates a downward force, increasing soil density. The static road roller does not have vibrating or oscillating mechanisms. It relies solely on its weight and gravity to achieve compaction. This method is effective for compacting cohesive soils and achieving a smooth, stable surface suitable for road construction and other applications.
Vibratory road rollers
Vibratory road rollers utilize both vibrations and the drums weight for compaction. The roller’s drum contains eccentric weights that rotate rapidly, creating vibrations. These vibrations are transferred to the material being compacted, causing the particles to rearrange and settle closely together. The high-frequency vibrations help in densifying the soil, eliminating air voids, and enhancing compaction efficiency. The vibratory action of the roller improves compaction in granular soils, and the amplitude and frequency of vibrations can be adjusted to suit different soil types and compaction requirements.
Operation of a Road Roller
Pre-operation checks
Before operating a road roller, important pre-operation checks must be conducted. These include inspecting the roller for any visible damage or leaks, checking fluid levels, ensuring proper tire inflation, testing brakes and lights, and verifying the functionality of controls and safety features.
Starting and control
To start a road roller, the operator typically follows these steps:
- Ensure the roller is in a safe and stable position.
- Activate the ignition switch or start button to start the engine.
- Engage the transmission by selecting the appropriate gear or mode.
- Gradually release the brake to allow movement. To control the road roller, the operator uses the steering wheel or joystick for directional changes, accelerator and brake pedals for speed adjustments, and hydraulic controls for activating vibrating or compacting mechanisms.
Compaction process
The compaction process requires attention to detail to avoid uneven compaction. The roller passes should be done along the straight and easily accessible direction. The passes should overlap to ensure no parts are left out. You should check the density of the material after every pass to ascertain the density.
Safety Considerations When Using a Road Roller
When using a road roller, several safety considerations must be taken into account. Operators should receive proper training on equipment operation and safety protocols. Personal protective equipment, such as helmets, high-visibility clothing, and safety shoes, should be worn. Clear communication with other workers and pedestrians is crucial. Adequate traffic control measures must be implemented.
Regular equipment maintenance and inspections are essential to ensure safe operation. Caution should be exercised around slopes, trenches, and unstable ground to prevent accidents or rollovers.
Maintenance and Care For Road Rollers
Maintenance and care for road rollers involve regular inspection and servicing to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This includes checking fluid levels, inspecting belts and hoses, examining tires for wear, and verifying the functionality of brakes and lights. Cleaning the roller regularly, removing dirt and debris, helps prevent corrosion.
Lubrication of moving parts is essential to reduce friction and promote smooth operation. Proper storage and transportation involve protecting the roller from weather elements and securing it during transportation to prevent damage.
Conclusions
Road rollers are vital machines in construction and road maintenance. Understanding their components, working principles, and safety considerations is crucial for efficient and safe operation.
Conducting pre-operation checks, following proper starting and controlling procedures, and adhering to maintenance and care practices ensure optimal performance and longevity. Road rollers play a key role in achieving compaction, improving surface stability, and creating uniform, durable surfaces.
By prioritizing safety and regular maintenance, road rollers contribute to successful construction projects and safe work environments.



















Leave A Comment