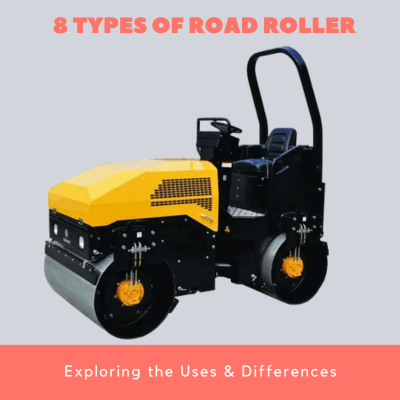
13 Types Road Roller: How to Choose a Right One-4 Factors
A. Definition and purpose of road rollers
The construction process involves using a variety of tools and equipment. While all these are geared towards improving construction quality, their applications vary. The equipment used in construction of foundations are not the same as those used in superstructure works.
Additionally, some equipment such as asphalt spreading machines are only applicable to road and pavement construction. Road rollers are some of the equipment that are applied universally in all types of construction. Road rollers have a critical role in road construction, structural construction and landscaping.
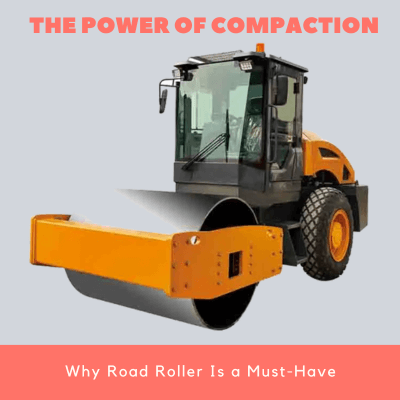
Road rollers comprise of a power generating mechanism; usually an engine, control unit, tires, and a weighted drum. Power generated by the engine pushes the drum over construction material to exert compaction force.
B. Importance of road rollers in construction and road maintenance
The key function of road rollers is compaction. Compaction is the elimination of air pockets and dense packaging of soil particles by application of an axial force. In building and construction, having stable bases ensures structural soundness and safety.
Road rollers are used in road construction to compact base and subbase layers for asphalt surfacing. Proper compaction prevents settling which may result in cracks and potholes formation. Pneumatic and smooth drum road rollers are used to provide an even and smooth asphalt surface for roads. This process ensures air is eliminated to prevent cracking due to expansion in hot seasons.
Foundations for buildings require stable grounds for safety; compaction is done using road rollers to achieve the needed stability. Improved density due to compaction increases the bearing capacity of foundation soils; this guarantees structural safety.
Contents
Static Road Roller
A. Definition and characteristics
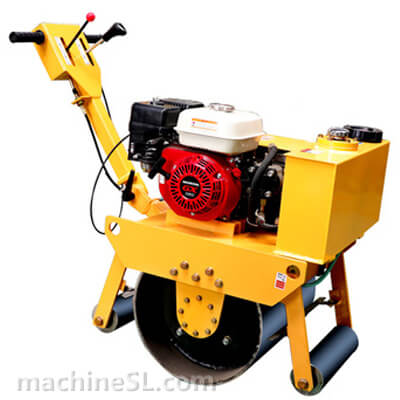
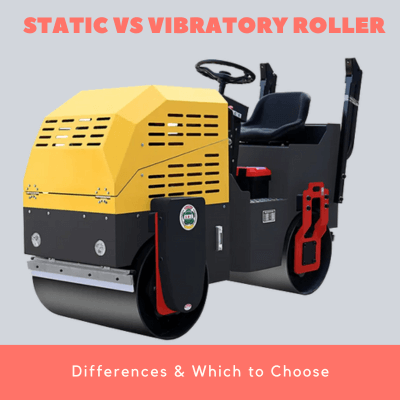
Static road rollers comprise of a drum, tires, and a driving mechanism; engine and the controls. They solely rely on the weight of the drum to exert compaction force. Static rollers have minimal movable parts compared to other types of rollers. This makes them affordable to acquire and cheap to maintain. They are mostly used to compact granular materials such as ballast.
B. Types of static rollers
1. Smooth wheeled rollers
This is the most common type of road roller used in construction today. It consists of a smooth drum mounted at the front or at the back. It has a wider range of applications, including landscaping. Smooth wheeled rollers are essential in providing even surfaces after compaction. They are commonly applied in base compaction for roads.
2. Padfoot or tamping rollers
They consist of a drum with pads/ feet arranged in an irregular pattern. The pads on the roller reduce the weight to surface area ratio generating more pressure per unit area on the compaction material. The pads are distributed in a manner that covers majority of the area under the drum during compaction.
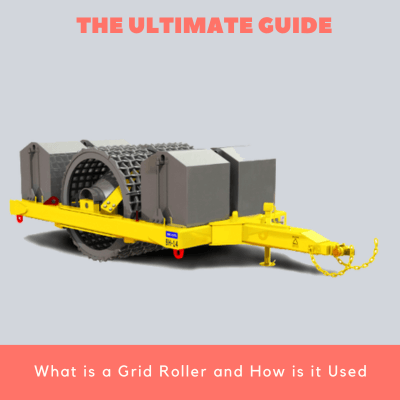
3. Grid rollers
Grid rollers are usually towed behind a vehicle. They could be mounted on a truck or on specially designed vehicles. Grid rollers are used where high contact pressure with material is required. The drum on the roller is fitted with steel bars that form a grid, hence its name. Grid rollers are suitable for compacting well graded coarse soils and weathered rocks.
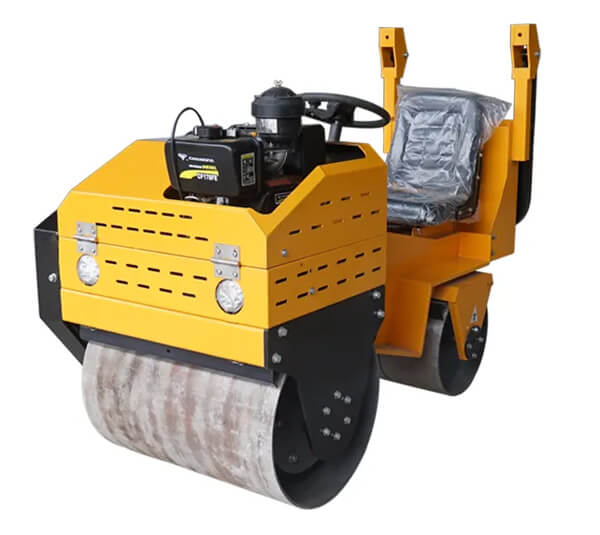
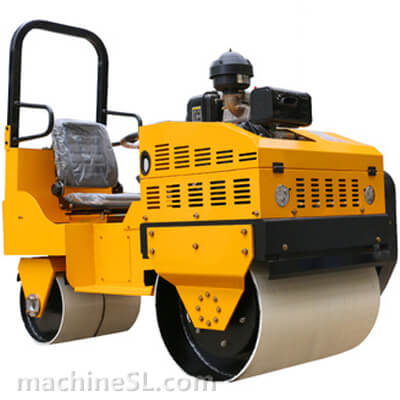
Vibratory Road Roller
A. Definition and characteristics
Vibratory road rollers are equipped with a vibration mechanism to facilitate more efficient compaction. In these rollers, the drum is fitted with suspended weights which when triggered vibrates. The vibration is transferred to the drum and to the material under compaction. Vibratory rollers eliminate air pockets faster than static rollers hence more effective for cohesive soils. The degree of vibrations can be adjusted depending on the required compaction results or working environment. If not used properly, vibratory rollers could cause damage to surrounding structures.
B. Types of vibratory rollers
1. Single-drum vibratory rollers
Single drum vibratory rollers consist of one drum mounted at the front or back of the cabin. The cabin is also fitted with pneumatic tires for navigation and stability during work. With its singular drum design, this type of roller enables efficient compaction across wide surface areas, making it an essential tool in achieving optimal density in road construction, pavement projects, and similar applications that require precise compaction control.
2. Double-drum vibratory rollers
Unlike single-drum rollers, this type of road rollers has no pneumatic tires, instead it has drums mounted both at the front and back of the cabin. Double-drum rollers deliver more compaction force due to the two drums; hence lesser passes are required. However, the absence of tires makes it hard to maneuver.
3. Combination vibratory rollers
A combination vibratory roller features multiple smooth drums for vibratory compaction and additional pneumatic tires for finishing and sealing the surface. This combination allows for efficient compaction of different materials, such as soil, asphalt, and aggregates, while providing improved traction and surface finishing.
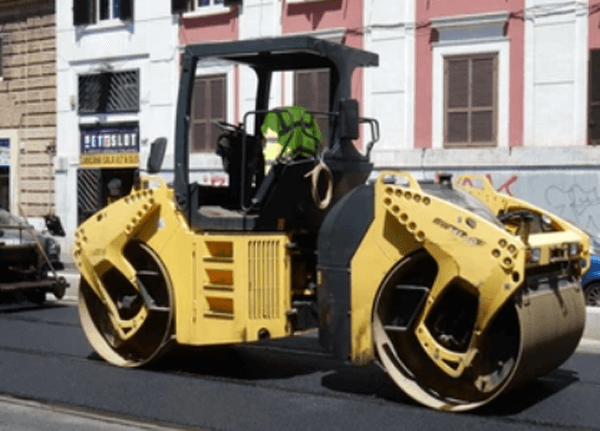
Pneumatic Road Roller
A. Definition and characteristics
Pneumatic rollers are specially designed for finishing works in asphalt paving. The rollers encompass rubber tires filled with air as the compaction interface. This roller type relies on its weight; the pneumatic air-filled rubber tires prevent damage to the surface. Pneumatic road rollers are engine powered with the operator cabin located in between the two sets of tires. The most common design of pneumatic rollers has four tires at the front and four at the back.
2. Grid rollers with pneumatic tires
This is a combination of both the grid roller and pneumatic roller. It has a drum with square steel grid that act as first contact with material under compaction. At the back, this roller type is fitted with air-filled rubber tires that smoothen the surface. These rollers are mostly used to correct compaction deficiencies in asphalt paving.
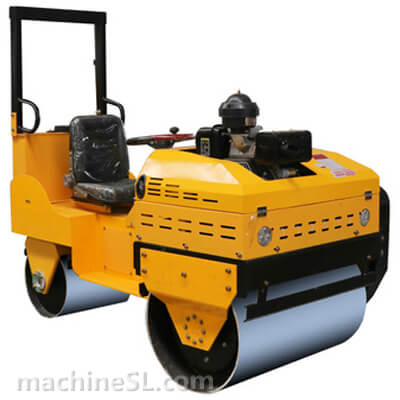
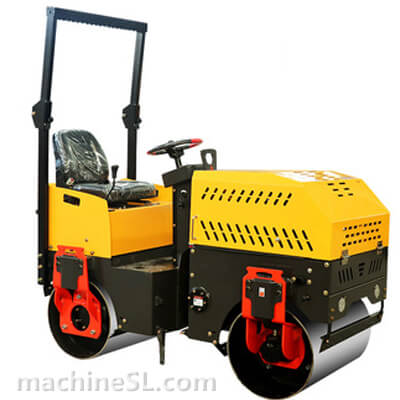
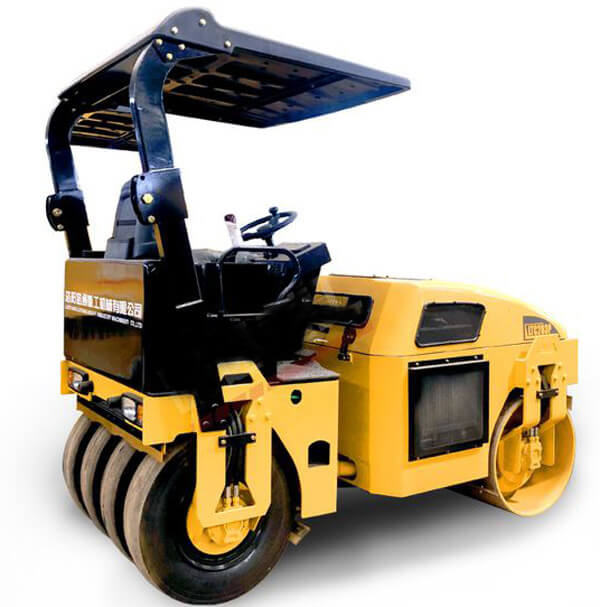
Tandem Rollers
A. Definition and characteristics
Tandem rollers consist of two steel drums positioned side by side on the front and rear axles. The drums rotate in opposite directions, providing compaction through static weight and vibration. These rollers are known for their high efficiency in achieving uniform compaction, especially on large-scale projects like road construction. Their characteristics include adjustable vibration frequency and amplitude, excellent maneuverability, precise control of compaction parameters, and the ability to compact both cohesive and granular materials.
B. Types of tandem road rollers
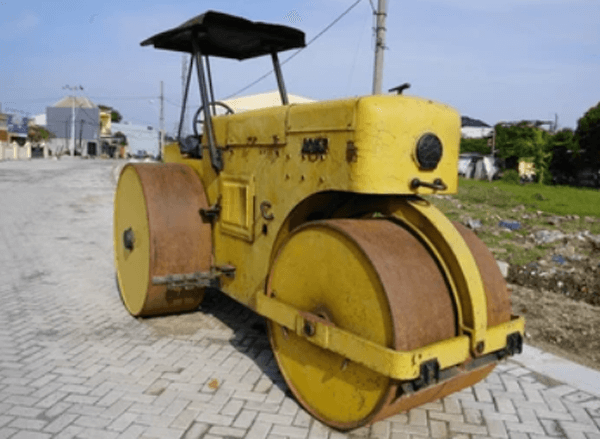
1. Smooth tandem rollers
These are tandem rollers with two static drums at the front and the back. The roller relies on the weight of the drums to exert compaction force. Smooth tandem rollers are mostly applied in asphalt surfacing or compaction of granular materials such as ballast.
2. Vibratory tandem rollers
This type of tandem rollers has suspended weights installed inside each of the drums. When triggered, the weights vibrate at a controllable frequency. The vibration is transferred to the material under compaction through the drum surface resulting in a higher degree of compaction. Vibratory tandem rollers are not suitable for surface smoothing as the vibrations tend to cause displacement of particles.
Instead, they are used to compact base and subbase layers in road construction.
Specialized Road Roller
A. Definition and features
These rollers are designed to perform functions that common types of rollers cannot. Characteristics of specialized road rollers include adjustable compaction parameters, such as vibration frequency, amplitude, and tire pressure. They often have excellent maneuverability and compact design to navigate tight spaces. Some models may feature water sprinkler systems to prevent material sticking, and others may have advanced control systems for precise compaction control.
B. Types of specialized road rollers
1. Chip spreader rollers
These are static smooth rollers with an added compartment for storing and spreading chips. The chips container is attached at the front with outlets opened and closed depending on the required amount. The width of the spreader can be adjusted depending on the construction requirements. Once the chips get to the ground, the roller passes over compacting them to required densities.
2. Reclaimer and stabilizer rollers
A reclaimer roller is designed to recycle and reclaim existing pavement materials, such as asphalt or cement, by pulverizing and mixing them with additional binding agents. The reclaimer features a large rotating drum equipped with teeth or blades that break up the existing pavement. The pulverized material is then mixed with water and other additives to create a stable base for road construction. This process helps reduce the need for new materials and promotes sustainability in road rehabilitation projects.
A stabilizer road roller, also known as a soil stabilizer or a soil stabilizer reclaimer, is used to stabilize and improve the properties of soil for road construction. It is particularly useful in areas with weak or poor-quality soil. The stabilizer roller features a powerful milling drum equipped with mixing paddles or blades. As it moves along the ground, the roller pulverizes the soil, mixes it with binding agents such as cement, lime, or specialized chemicals, and compacts it to create a stronger and more stable foundation.
3. Landfill compactors
These rollers are designed to compress and compact waste materials in landfills, reducing their volume and creating more space for additional waste disposal. They typically feature large steel wheels or pads that exert high pressure on the waste to enhance compaction. Landfill compactors also have enclosed cabins to protect operators from hazardous gases and odors.
Their purpose is to maximize landfill capacity, reduce environmental impact, and ensure efficient waste disposal operations.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Road Roller
A. Project requirements
Moisture content and soil density are the main compaction requirements in construction. The roller one chooses should be able to deliver the required soil conditions after compaction while maintaining economic feasibility of the project. Where a higher density and lower moisture and air content is needed, vibratory rollers are ideal.
B. Soil conditions
The type of soil dictates the type of roller to be used. Granular soils are best compacted with static rollers to avoid displacement. Cohesive soils have a higher water and air retention rate; therefore, vibratory road rollers are the best option for such soils.
C. Desired compaction results
The aim of compaction determines which roller to be used. For subbase layers in roads, a higher degree of compaction is needed to sustain traffic loads. Therefore, padded road rollers and grid rollers are used to deliver maximum compaction pressure.
D. Operational efficiency
Operation efficiency depends on the construction site terrain and roller type used. Tandem rollers have less maneuverability; thus, they cannot be used in steep slopes or sharp bends.
Conclusions
There are several types of road rollers. These include vibratory rollers, static rollers, tandem rollers, and specialized rollers. The choice of a road roller depends on project requirements, soil conditions, desired compaction results and operational efficiency of the roller. It is important to select the right roller for a project as it directly impacts the compaction results.
Additionally, the choice of rollers determines resources one spends on compaction. Technological advancements and new needs for compaction leads to invention of newer types of road rollers.
Specialized road rollers such as chip spreaders and reclaimers tend to lower construction costs by combining roles that would have otherwise been done by two separate equipment. This shows that road rollers will be around for the future of construction.




























Leave A Comment