Safety to Operate Rebar Bender Machine – 6 Tips From Pro
The construction industry is one of the most dangerous industries in the world. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, construction workers are 10 times more likely to be killed on the job than workers in other industries. One of the leading causes of construction accidents is the improper use of machinery.
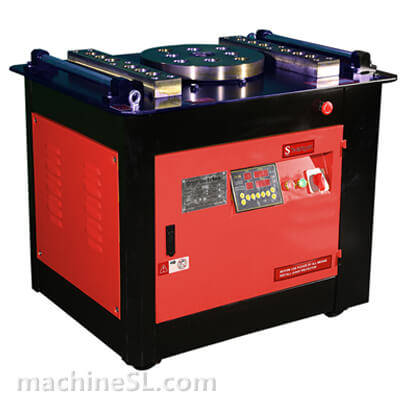
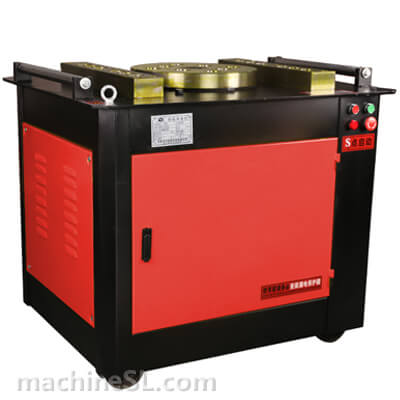
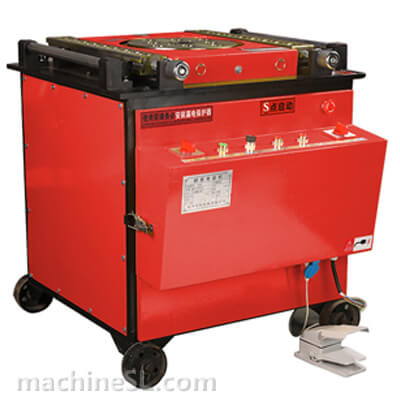
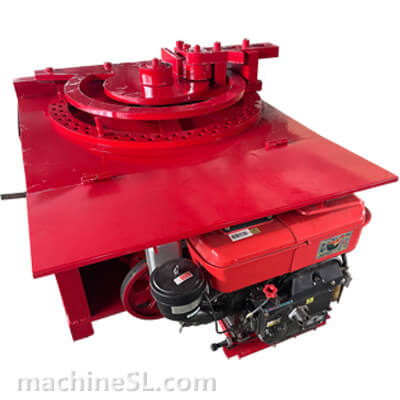
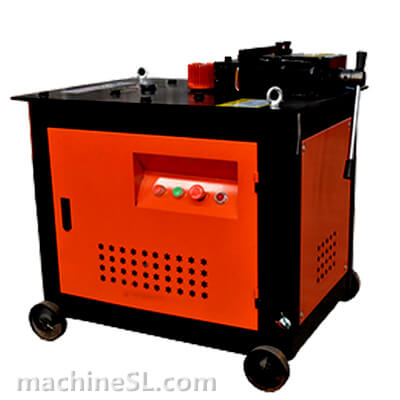
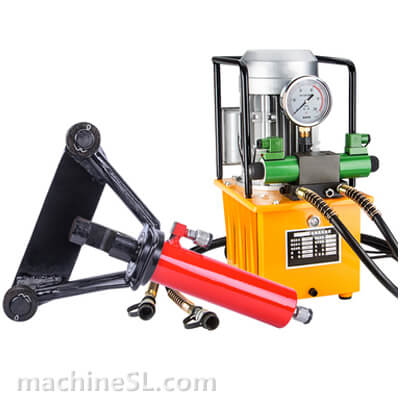
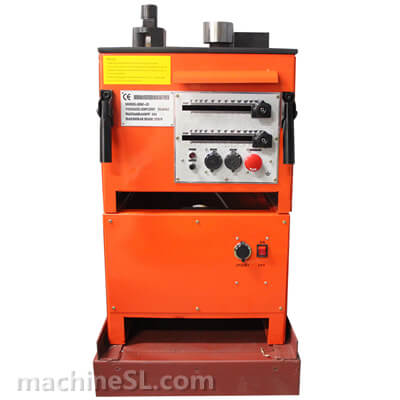
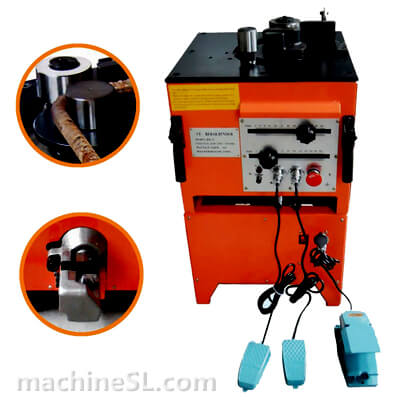
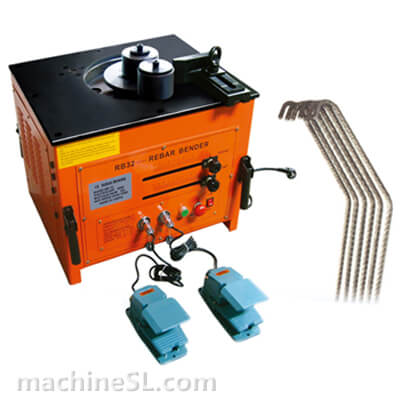
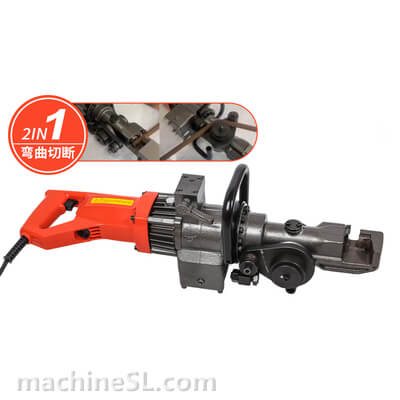
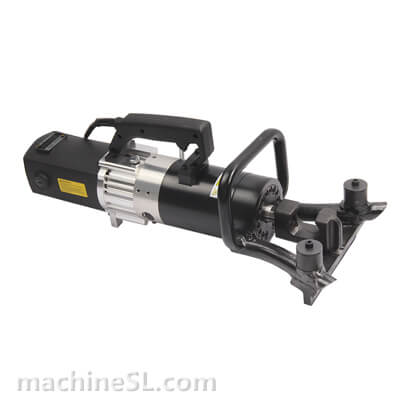
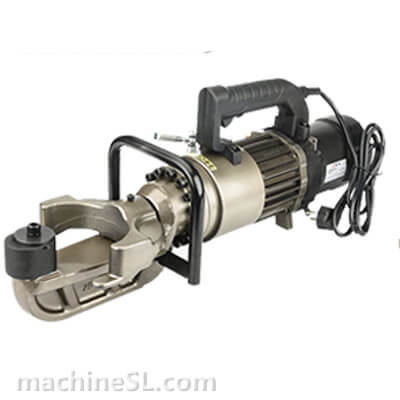
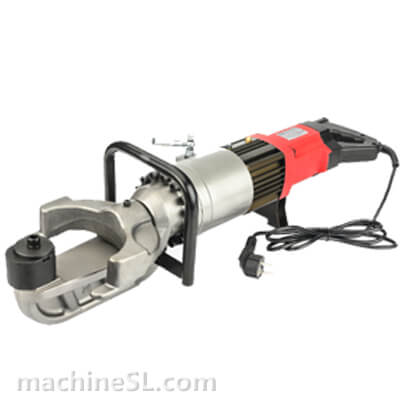
A rebar bender machine is a tool used to bend rebar, which is a type of steel reinforcement used in concrete. Rebar bender machines can be either manual or electric. Manual rebar benders are powered by the operator’s muscle strength, while electric rebar benders are powered by a motor.
Contents
Understanding the Rebar Bender Machine
The purpose of a rebar bender machine is to bend rebar to the desired angle. Rebar is typically bent to create curved shapes, such as arches or circles. Rebar bender machines can also be used to straighten rebar that has been bent or damaged.
Components and Mechanics of the Machine
The main components of a rebar bender machine are the frame, the bending mechanism, and the safety guards. The frame is the base of the machine and provides support for the other components. The bending mechanism is the part of the machine that actually bends the rebar. The safety guards are designed to protect the operator from injury.
Common Types of Rebar Bender Machines Available in the Market
There are two main types of rebar bender machines: manual and electric. Manual rebar benders are the most basic type of rebar bender. They are relatively inexpensive and easy to use. However, they can be difficult to use for large or heavy rebar. Electric rebar benders are more powerful than manual rebar benders. They are also easier to use for large or heavy rebar. However, they are more expensive than manual rebar benders.
Safety Features of Rebar Bender Machines
A. Automatic shut-off mechanisms
Automatic shut-off mechanisms are designed to stop the machine if the operator loses control of the rebar. This can help to prevent serious injuries.
B. Emergency stop buttons and switches
Emergency stop buttons and switches are designed to stop the machine immediately in the event of an emergency. They are typically located in a convenient location for the operator to reach.
C. Safety guards and protective barriers
Safety guards and protective barriers are designed to protect the operator from injury. They typically cover the bending mechanism and other moving parts of the machine.
D. Overload protection and warning systems
Overload protection and warning systems are designed to prevent the machine from being overloaded. This can help to prevent damage to the machine and serious injuries to the operator.
Compliance with Safety Standards
A. International safety standards and regulations
There are a number of international safety standards and regulations that apply to rebar bender machines. These standards and regulations are designed to ensure the safety of operators and users.
B. Importance of certification and testing
Rebar bender machines should be certified and tested to ensure that they meet the applicable safety standards and regulations. Certification and testing can help to ensure the safety of operators and users.
C. Examples of safety certifications for rebar bender machines
There are a number of safety certifications that are available for rebar bender machines. Some of the most common safety certifications include CE, CSA, and OSHA.
Training and Safe Operation
A. Proper training and qualifications for operators
Operators of rebar bender machines should have the proper training and qualifications. This training should cover the safe operation of the machine, as well as the applicable safety standards and regulations.
B. Understanding the machine’s operational manual
Operators of rebar bender machines should understand the machine’s operational manual. The operational manual will provide instructions on how to safely operate the machine, as well as warnings about potential hazards.
C. Precautions and safety guidelines for operating the machine
Operators of rebar bender machines should follow all precautions and safety guidelines when operating the machine. These precautions and guidelines will help to prevent serious injuries.
Potential Hazards and Risk Mitigation with Rebar Benders
The use of rebar benders in construction comes with inherent hazards. It is essential to identify these potential risks and implement appropriate risk mitigation measures to ensure the safety of operators and other personnel involved. Here are some common hazards associated with rebar benders and strategies for risk mitigation:
Mechanical Hazards
Hazard: Moving parts of the rebar bender, such as bending rollers or plates, can pose a risk of entanglement or crushing.
Risk Mitigation: Install safety guards and shields to prevent access to moving parts during operation. Operators should receive proper training on safe operating procedures, including keeping hands and clothing away from the bending mechanism.
Electrical Hazards
Hazard: Electric rebar benders carry the risk of electrical shock or electrocution if not properly grounded or if there are faulty electrical components.
Risk Mitigation: Ensure that the rebar bender is correctly grounded and that all electrical connections are secure. Regular inspections of electrical components should be conducted, and any issues should be addressed promptly by qualified personnel.
Ergonomic Hazards
Hazard: Improper ergonomics during rebar bending tasks can lead to musculoskeletal injuries, such as strains and sprains.
Risk Mitigation: Provide training to operators on proper lifting techniques, body mechanics, and ergonomics. Encourage the use of mechanical lifting aids or ergonomic tools to reduce physical strain. Regular breaks and rotation of tasks can also help prevent fatigue-related injuries.
Material Hazards
Hazard: Rebar can have sharp edges that may cause lacerations or puncture wounds. Flying debris during the bending process can also pose a risk to operators and bystanders.
Risk Mitigation: Operators should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, gloves, and steel-toed boots, to protect against potential injuries. Regular inspection of rebar for defects or sharp edges is crucial, and damaged or sharp-ended rebar should be handled and disposed of properly.
Pinch Points and Crush Hazards
Hazard: Pinch points and crush hazards can occur when feeding rebar into the bending mechanism or during the bending process.
Risk Mitigation: Operators should be trained on proper rebar feeding techniques, ensuring that fingers and hands are kept clear of pinch points. Adequate space should be maintained around the rebar bender to avoid crushing hazards, and personnel should not lean or place body parts in the path of moving parts.
Operator Training and Supervision
Hazard: Insufficient training and inadequate supervision can lead to unsafe practices and increased risks.
Risk Mitigation: Provide comprehensive training to operators on the safe operation of rebar benders, including hazard awareness, proper procedures, and emergency protocols. Regular supervision and monitoring of operators’ performance and adherence to safety protocols are vital for maintaining a safe work environment.
Maintenance and Inspections
Hazard: Lack of regular maintenance and inspections can result in malfunctioning equipment, increasing the risk of accidents.
Risk Mitigation: Establish a routine maintenance schedule for rebar benders and conduct regular inspections to identify and address any potential hazards or mechanical issues promptly. Only trained and qualified personnel should perform maintenance and repair tasks.
Effective hazard identification, risk assessment, and mitigation strategies are essential for the safe operation of rebar benders. Providing adequate training, enforcing safety protocols, and maintaining equipment in good working condition significantly reduce the risk of accidents
User Reviews and Industry Insights
A. Gathering feedback from operators and users
Rebar bender machines are used by a wide range of people, including construction workers, contractors, and engineers. There are a number of online forums and websites where operators and users of rebar bender machines can share their feedback. This feedback can be helpful in identifying potential hazards and risk mitigation strategies.
B. Industry recommendations and best practices
There are a number of industry organizations that have developed recommendations and best practices for the safe use of rebar bender machines. These organizations include the American Society of Safety Engineers (ASSE), the Construction Industry Institute (CII), and the National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA).
C. Case studies highlighting the safe use of rebar bender machines
There are a number of case studies that have been published that highlight the safe use of rebar bender machines. These case studies can provide valuable insights into the potential hazards associated with these machines and how to mitigate these risks.
Here is an example case study
- “A construction worker was injured when his hand was caught in a rebar bender machine. The worker was not wearing safety glasses, and he was not following the safety instructions. The worker suffered serious injuries, including a broken arm and a laceration to his eye.”
Conclusions
Rebar bender machines are a valuable tool for construction workers and contractors. However, it is important to operate these machines safely to prevent serious injuries.
Rebar bender machines can be a safe tool when used properly. However, there are a number of potential hazards associated with these machines, such as pinch points and entanglement risks. It is important to be aware of these hazards and to follow the safety instructions to help prevent serious injuries.
I hope this article has been helpful. Thank you for reading!











































Leave A Comment