Demystifying Rebar Bender Jobs: A Comprehensive Guide
Rebar bender jobs involve the skilled operation of machinery or tools to shape and bend reinforcement bars (rebars) used in concrete structures. These jobs are crucial in the construction industry as they ensure the proper alignment, configuration, and strength of rebars, contributing to the structural integrity and durability of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
The demand for rebar bender jobs remains high due to the increasing scale and complexity of construction projects, requiring the expertise of qualified rebar benders to accurately bend rebars according to project specifications, safety regulations, and quality standards.
Their precision and skill play a vital role in creating safe and long-lasting structures.
Contents
Overview of Rebar Bending
The rebar bending process involves shaping and bending reinforcement bars (rebars) to the desired angles and configurations required for construction projects. This is typically done using specialized machinery or manual tools. The rebars are carefully measured and positioned before applying force to bend them into the desired shape, ensuring they fit precisely within the concrete structure.
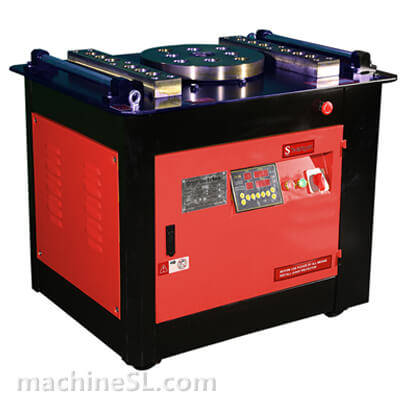
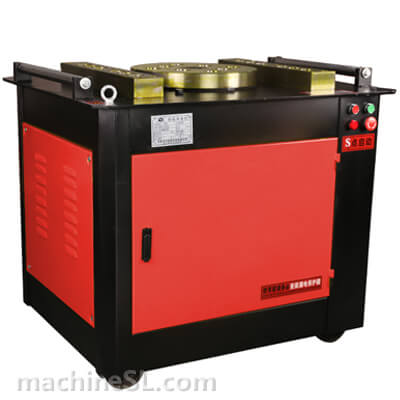
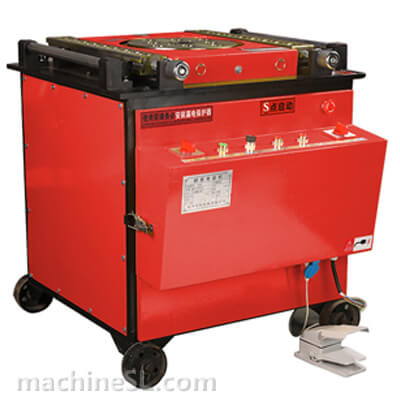
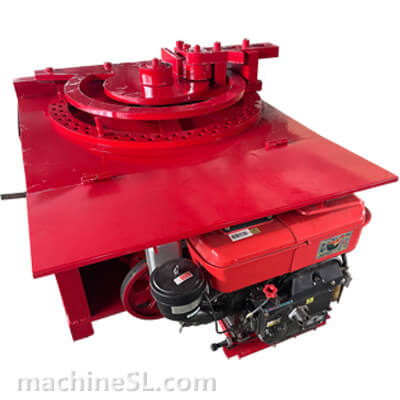
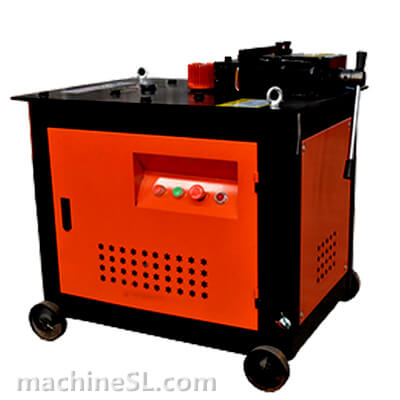
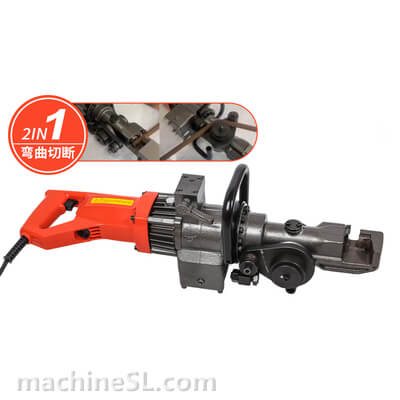
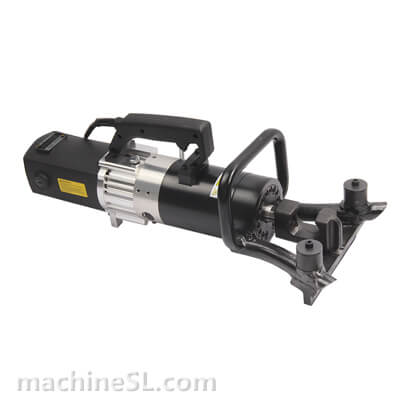
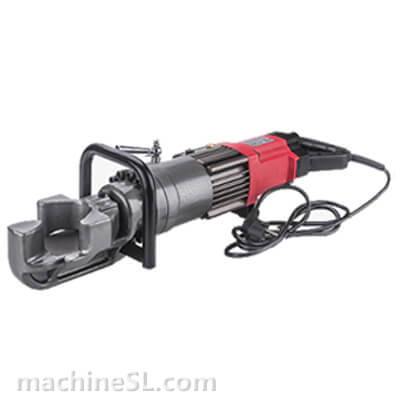
Types of rebar benders used in the industry
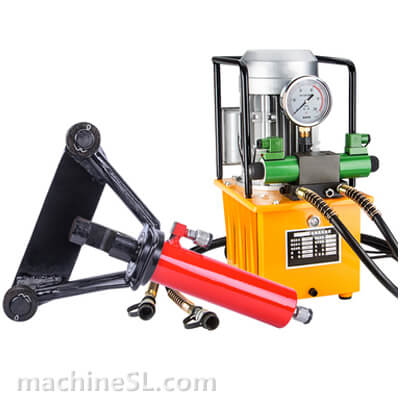
There are various types of rebar benders used in the industry, including hydraulic benders, electric benders, and manual benders.
- Hydraulic benders are commonly used for heavy-duty bending, offering high power and precision.
- Electric benders are suitable for lighter bending tasks, providing convenience and efficiency.
- Manual benders require physical effort and are used for smaller-scale projects or in areas where access to power is limited.
Safety precautions and guidelines are crucial when performing rebar bending. Workers should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety goggles, gloves, and steel-toed boots, to protect against potential hazards.
It is important to follow proper lifting techniques to avoid strain or injury. The work area should be clear of debris, and workers should be cautious of their surroundings. Regular inspection and maintenance of bending equipment are necessary to ensure safe operation.
Job Responsibilities of a Rebar Bender
- As a rebar bender, one of the primary responsibilities is reading and interpreting construction blueprints and plans. This involves understanding the design specifications and identifying the locations where rebars need to be bent and installed.
- Cutting and bending rebar to specified dimensions is another key responsibility. Using appropriate tools and machinery, rebar benders accurately measure, mark, and cut rebars to the required lengths. They then use bending equipment to shape the rebars according to the specified angles and configurations indicated in the plans.
- Operating rebar bending machinery and tools is an essential part of the job. Rebar benders are skilled in safely and effectively using hydraulic benders, electric benders, or manual tools to bend rebars to the desired shapes. They must ensure precise bending to meet the project requirements.
- Collaboration with the construction team and supervisors is necessary. Rebar benders work closely with architects, engineers, contractors, and other construction professionals to coordinate and align their work with the overall project schedule. They take direction from supervisors and communicate any challenges or issues that may arise during the bending process.
- Ensuring compliance with building codes and regulations is a crucial responsibility. Rebar benders must have knowledge of relevant building codes and regulations to ensure that the bending work meets the required standards for structural integrity and safety. They also need to follow any specific guidelines or quality control procedures set by the construction project or regulatory authorities.
Required Skills and Qualifications
- Physical strength and dexterity are essential skills for rebar benders as the job often involves lifting and manipulating heavy rebar materials and operating bending machinery.
- Familiarity with construction materials and techniques is important for understanding the characteristics and properties of rebars, as well as their role in concrete structures.
- The ability to read and interpret construction drawings is crucial for understanding the bending requirements, angles, and configurations specified in the plans.
- Knowledge of rebar bending machinery and tools is necessary to safely and effectively operate hydraulic benders, electric benders, or manual tools to shape rebars accurately.
- Attention to detail and accuracy are vital skills as rebar benders must precisely measure, mark, and bend rebars to meet the specified dimensions and angles.
- Communication and teamwork skills are important for collaborating with the construction team, architects, engineers, and supervisors to ensure coordination and alignment with project requirements.
- Understanding safety protocols is crucial for maintaining a safe work environment. Rebar benders should be knowledgeable about safety regulations, PPE requirements, and safe operation of machinery to prevent accidents and injuries.
Training and Education
- Rebar bender positions typically do not have strict formal education requirements. However, a high school diploma or equivalent is commonly preferred by employers. Basic math skills and the ability to read and interpret construction drawings are important.
- On-the-job training and apprenticeship programs are common paths for individuals aspiring to become rebar benders. These programs provide hands-on experience and mentorship under the guidance of experienced professionals. Apprenticeships typically last several years and combine practical training with classroom instruction.
- Certification and licensing options are available for rebar benders, although they may not be mandatory in all jurisdictions. Organizations such as the Concrete Reinforcing Steel Institute (CRSI) offer certification programs that validate the skills and knowledge of rebar benders. These certifications can enhance job prospects and demonstrate a commitment to professional development. Additionally, some states or countries may require rebar benders to obtain a specific license or registration to work in the construction industry. Checking with local regulatory authorities is important to understand any specific certification or licensing requirements.
Job Outlook and Salary
- The demand for rebar bender jobs in the construction industry remains steady. As construction projects continue to be undertaken worldwide, the need for skilled rebar benders who can ensure the structural integrity of concrete structures remains essential.
- The projected growth and opportunities for rebar benders vary based on regional construction activity and infrastructure development. Growing urbanization, renovation projects, and new construction initiatives can create employment opportunities for rebar benders. Additionally, advancements in construction technology and the use of prefabricated components may also influence the demand for rebar benders.
- The average salary range for rebar benders can vary depending on factors such as experience, location, and the complexity of projects. In general, rebar benders earn a competitive salary. Entry-level positions may have lower starting salaries, but with experience and expertise, rebar benders can earn higher wages. It is important to note that salary ranges can vary significantly by country, region, and prevailing economic conditions.
Career Development and Advancement
- Rebar benders can progress from entry-level positions to senior roles with experience and expertise. They may take on more complex projects, supervise and train junior rebar benders, or move into managerial positions where they oversee rebar bending operations on a larger scale.
- Continuing education and specialized training options can enhance career development for rebar benders. They can pursue courses or certifications in advanced rebar bending techniques, construction management, project planning, or safety management. Staying updated with the latest industry practices and advancements can open up opportunities for career growth and advancement.
- Rebar benders have potential career paths within the construction industry. They can specialize in rebar bending and become highly skilled experts in their field. Alternatively, they may explore related roles such as construction supervisors, project managers, or estimators, leveraging their knowledge and experience in rebar bending to contribute to the overall construction process. With additional education and experience, some rebar benders may even choose to start their own construction businesses or consulting firms.
Conclusions
Rebar bender jobs play a vital role in the construction industry, ensuring the structural integrity and strength of concrete structures. With a high demand for skilled rebar benders, their expertise in accurately bending and shaping rebars is crucial for creating safe and durable buildings and infrastructure.
The job responsibilities of a rebar bender include reading construction plans, cutting and bending rebars, operating machinery, and ensuring compliance with safety protocols. Skills such as physical strength, attention to detail, and communication are important, while formal education requirements can vary.
Aspiring rebar benders are encouraged to consider on-the-job training, apprenticeship programs, and certification options to develop their skills and enhance career prospects. With dedication and continuous learning, a career as a rebar bender offers opportunities for growth and advancement within the construction industry.











































Leave A Comment